The updated Kaspersky SIEM now features AI functionality for detecting signs of DLL hijacking attacks, improving detection efficiency.
Dynamic link library (DLL) hijacking is a common technique in which attackers replace a library loaded by a legitimate process with a malicious one.
It is used by creators of mass-impact malware, like stealers and banking Trojans, as well as by APT (advanced persistent threat) and cybercrime groups behind targeted attacks.
Kaspersky has observed this technique and its variations, like DLL sideloading, in targeted attacks on organizations in Russia, Africa, South Korea, as well as other countries and regions.
To further enhance its protection capabilities against this threat, Kaspersky SIEM has introduced a specialized AI-based subsystem that continuously analyzes information about all loaded libraries.
The new feature has already proven effective, helping to detect an attack by the APT group ToddyCat.
It enabled the threat to be identified and blocked at an early stage, preventing any impact on the targeted organizations.
The model also uncovered attempts to infect potential victims with an infostealer and a malicious loader.
“We are seeing DLL hijacking attacks become more common, where a trusted program is tricked into loading a fake library instead of the real one.
This gives attackers a way to secretly run their malicious code.
This technique is difficult to detect, and this is where AI can help.
Using advanced protection techniques empowered with AI is now essential to staying ahead of these evolving threats and keeping critical systems safe,” says Anna Pidzhakova, Data Scientist at Kaspersky’s AI Research Center.
Securelist has published two related articles: the first explains how a machine-learning model was developed to detect DLL hijacking attacks, while the second describes how this model was integrated into the Kaspersky SIEM platform.
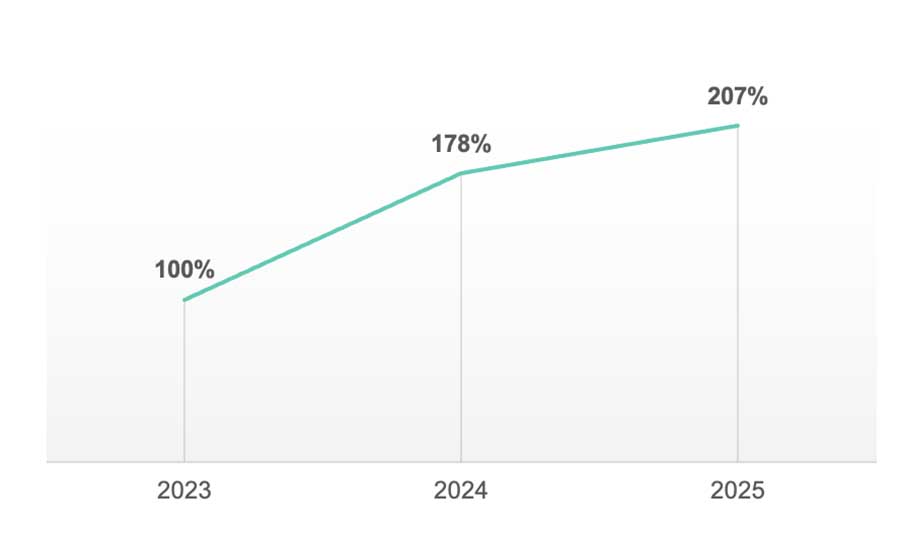
Photo Caption : The number of DLL hijacking attacks and their variations in 2023-2025 (Source: Kaspersky Security Network)